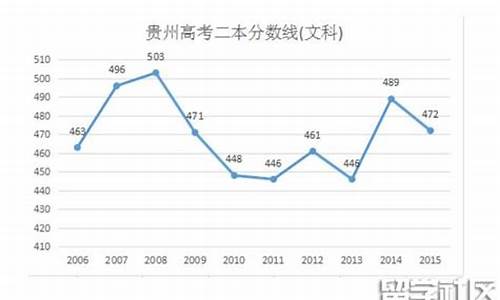
您现在的位置是: 首页 > 录取信息 录取信息
高考英语试卷字体字号标准,高考英语试卷
tamoadmin 2024-05-22 人已围观
简介您好,对于你的遇到的问题,我很高兴能为你提供帮助,1猜题思路分析从近三年来全国及各省高考英语试卷“完形填空”试题的命制,基本上遵循了“突出语篇,强调应用,注重实际”的设计思路。试题特点鲜明———-“考查考生在阅读理解的基础上对词汇知识的掌握情况”,即要求考生通读短文,掌握文章大意,综合运用所学的词汇、语法等知识,从试题所提供的词汇、短语中判断出使短文意思通顺、结构完整的词汇或短语,在语篇中考查学生
您好,对于你的遇到的问题,我很高兴能为你提供帮助,
1猜题思路分析
从近三年来全国及各省高考英语试卷“完形填空”试题的命制,基本上遵循了“突出语篇,强调应用,注重实际”的设计思路。试题特点鲜明———-“考查考生在阅读理解的基础上对词汇知识的掌握情况”,即要求考生通读短文,掌握文章大意,综合运用所学的词汇、语法等知识,从试题所提供的词汇、短语中判断出使短文意思通顺、结构完整的词汇或短语,在语篇中考查学生的语言知识灵活运用能力。完形的选材通常是记叙文或夹叙夹议的文章,内容情节深刻,常涉及人物心理活动方面的细致描写,篇章与句子结构变化丰富,文章内容健康、时尚,将知识、文化、教育、趣味融为一体,即:时代感突出,生活化明显,寓教于乐。以后完形填空将会继续朝着语言交际化、情景生活化、词汇运用灵活化的方向发展。
2完形填空的命题特点
完形填空是一种测试学生语言水平和实际运用语言能力的综合性题型,它要求学生掌握词汇知识,习惯用语,语法知识,句法结构,而且要有一定的语篇领悟能力,逻辑思维能力和语言感悟能力,是综合了现行的单选和阅读的考查,特别强调对语篇及上下文的理解和应用。
1
完形填空所考查的能力:
词汇(词的基本用法、词的搭配和习惯用语、同义词/近义词/形似词的区分)语法(句型结构分析)
阅读理解能力(快速阅读、找中心句和理顺文章结构)
推理、分析、判断、归纳概括能力
背景知识和生活常识
2
完形填空的命题特点
1.高考完形填空试题材料的词汇量比以前有所增加,文章的难度也相应增大,考查由局部理解向整体理解转移,增加了语篇理解的试题,设问角度突出考查对上下文乃至全篇的理解。
2.试题考查点减少了单句层次的试题,淡化语法,而被情景选择所取代。
3.文章体裁仍以记叙文或夹叙夹议为主,选材体现时代性、思想健康。在布空方面以实词为主,其中以动词、名词、形容词、副词为核心,另外,选项具有有效性和干扰性,充分体现语言知识灵活运用的特征。
4.对民族文化和语言背景知识的考查加大。
3完形填空解题步骤
总则:在把握整篇文章的基础上对句子内部的情况进行分析。
1.必读首尾句,预测主题,判断文体
完形填空短文无标题,首句不设空,所以要必读首句。另外,学生还要认真读第二段的首句,第一段的尾句及整篇文章的尾句(文章的主题句有时在第二自然段的句首,有时在第一自然段的句尾或整篇文章的句尾)。
记叙文:首句交待4个W(when, where, who , what);
说明文:首句提出/解释说明某事物;
议论文:首句提出一个论点;
2.跳读全文,领会大意
借助首尾句提示,跳过空格,快速把短文从头至尾读一遍,进一步从整体上理解短文大意。
3.通读全文,试选答案
抓住上下文内容联系和逻辑关系,把所给4个选项分别放入空格所在句子中试填,弄清空格处待填的是什么词,起何作用,同时注意习惯表达及语法知识。
4.细读全文,推敲难题
根据常识,运用逻辑推理,结合语境和已选答案提供的信息,对难的备选项仔细推敲。
如实在难以确定,采用“排除法”,首先排除在语法/内容上明显不符合要求的答案,再对剩下的选项比较。
5.复读全文,调整答案
把所填的答案代入空格,检查所选答案是否能使文章上下连贯,前后照应,逻辑合理(对于模棱两可的答案,最好尊重第一印象,不改动为好;实在不能解决的空格,只能凭语感来选择)。
4完形填空解题方法及备考策略
一. 词汇知识的运用(各类词的用法及搭配、词语辨析)
1.动词
1)动词的结构功能(vi./vt./linkv., 接什么样的宾语,能否接复合宾语,接什么样的复合宾语)
eg (1). But by using literary texts alongside other texts, teachers can 42 students improve their reading skills.
A. force B. help C. get D. wish
析:选B。只有help 可接help sb.do sth.
2)分析上下文情景,注意词汇与话题的同现
结构是为意思服务的,在完形填空中大部分选项只看动词的结构功能是很难判断的,所以要分析上下文情景。
(2)(Father)“Kate and John, a friend of mine is coming here to see me this evening, and I wish to be with him. Will you go up to your own room?”We ,went to our room and closed the door.
A. punished B. trembled C. obeyed D. replied
析:C上文父亲吩咐她们上楼到自己的房间去,她们去了,说明按父亲的吩咐做了,所以选C。
2.代词(不定代词/指示代词; 人称代词/物主代词/反身代词/疑问代词/关系代词/相互代词等)
1.不定代词(some, any, no, somebody, anybody, nobody, no one, one, none, something, anything, nothing ; all, every, each, other, either, neither, both, half, everybody, everyone, everything ; many, much, few, little, a few等)
2.指示代词(that, this, these, those, such ,same, so one 代[C] 泛指,指非限定的一个;可代人/物
that 代[C] 特指;不可代人;代[U]
this 近指,后指 that 远指,前指
(3) is the sports programme. 开始体育节目。
(4) is the end of the news. 新闻到此结束。
Keys: (3)This 4)That
3.名词/形容词/副词/介词(依上下文语义/语境要求,搭配,话题来选)
4.同义词/近义词/形似词
1)词的搭配能力(rise/raise, hope/wish)
如:demand (of sb.) to do sth. pick one’s pocket request/require sb. to do sth. rob sb. of sth. steal sth. from sb.
2)单词的适用范围/场合
如:voice/sound/noise; defend/protect/guard ,ask/beg,kill/murder等
3)单词的感情色彩
如:die 中性词,pass away 表示对死者的尊敬
4)过程与结果的不同
look for/search 重过程 find/discover 重结果
5)区分结构类似而意思不同的表达法
如:be used to do sth./be used to doing sth./used do sth.
take place/take one’s place/take the place of can’t help do sth./can’t help doing sth./can’t help but do sth.
6)注意有意识与无意识
如:notice:表无意识行为,observe/watch/see 表有意识行为
5词语的搭配
1)动词的搭配(do 和make的搭配能力较强,要常记,记牢,记熟)
do(a job, work, shopping, cooking, reading, typing, sewing, good, wrong, damage, harm, a favor, an injury, etc.)
make(a study, an appointment, arrangements, a breakthrough, a call, a comparison, contribution, a deal, a decision, a discovery, distinction, a guess, preparations, a start, a start, a survey, an attempt, an error, a profit, a fortune, a living, one’s way, sense, point, peace, bed, coffee, a fuss, etc.)
2)名词的搭配
形容词与名词的搭配有的具有一定的文化背景,学生要注意“貌合神离”的词语。如:
lucky dog 幸运儿 right hand得力助手narrow escape死里逃生 dark horse出人意料的获胜者
3)形容词的搭配
有些形容词可以加一个形容词修饰,表示强调,使表达更加生动。常见的有:pitch dark(漆黑的), brand new (崭新的),crystal clear(水晶般的) ,wide open(张得大大的), fast asleep(睡得很熟的), wide awake(完全醒着的), icy cold(冰冷的), etc.
有些形容词可以和不同的介词搭配,学生应注意比较、归纳。如:
sick for 渴望 tired from因 而疲劳 engaged in 忙于
sick of 厌倦 tired of 对 厌倦 engaged to 与某人订婚
篇章技巧的运用
一个完整的语篇,一篇内容充实、结构合理、行文流畅的短文所依赖的不只是词汇和语法,更多的是篇章结构技巧。作者借助于篇章技巧成文,学生在复现作者的语言时同样可以借助篇章技巧。
1.复现
“词汇的复现”是指某一词以原词、同义词/近义词、反义词、同源词、概括词(总分关系)以及其他形式重复出现在语篇之中。词汇复现的语用意义是使得语篇中的句子相互衔接和连贯,从而构成一个完整和有机的意义整体。大体上说,词汇的复现包括:原词复现、同义词/近义词复现、反义词、同源词复现、概括词复现和注释性复现(其中一种表达是对另一种的解释)。具体指某一词以原词,指代词,同义词,反义词、同源词、概括词等重新出现在整个文章的前后,并起到了衔接全文的作用。
(5)First of all he was a window-cleaner and in his first week he managed to six windows.
A. rub B. drop C. break D. clean
析:D同源词复现,由window-cleaner可知为clean the window.
2. 同现
同现指意义上相互联系的单词同时出现在同一语篇中。一个语篇,一个话题,要求有与之相连的词汇(篇章中的词汇链)。
1) 名词同现:与一个话题或一个名词出现在同一个语境的另一个名词。如:
school---primary school—middle school—college—university
students—pupils—graduates—postgraduates
2) 动词同现:与一个话题或一个名词出现在同一个语境的另一个动词。如:
school—teach—learn—attend—found—drop out—graduate—be dismissed
3)形容词同现
就某一语境而言所能出现的形容词也是有规律的。如:在学校这个语境中:(key)school—(optional)course—(compulsory)course
4) 结构同现
结构同现批搭配之类的句型和成对出现的短语。如:
some…,others; on one hand…,on the other hand; former…,latter; so…that; not only…but also; hardly/scarcely…when…; no sooner…than…; be about to do /be doing /had done /be on the point of doing/be to do/be ready to do/be on the way … when…; (6)I put my head in, expecting the (worst). But to my (surprise), the room wasn’t empty at all. It had furniture, curtains, a TV, and even paintings on the wall. And then on the well-made bed sat Amy, my new __44__, dressed neatly.
A. roommate B. classmate C. neighbor D. companion
析:A名词同现,从room, furniture,等同现信息可知。
(7)We were __42____ to go back for class again when the headmaster called us ( together) and said, …42. A. about B. able C. sorry D. sure
析:A结构同现,be about to do …when…
3.逻辑关系
一个完整的语篇应该是符合逻辑的,文章逻辑关系的取得主要靠过渡词的使用。作者利用转承语保证文章的逻辑,学生在做完形填空时应通过自己对上下文的理解,找到适当的逻辑关系,然后选择正确的过渡词。学生必掌握常见的过渡词:
1.递进
in addition, furthermore, again, also, besides, moreover, what’s more, what’s worse, to make matters worse , to make things worse , worse still
2.比较
in the same way, as with, similarly, equally, in comparison, just as
3.对照
in contrast, on the other hand, instead, however, nevertheless, unlike, on the contrary, while
4.因果
because, because of, for, since, due to, owing to, thanks to, as a result (of), so, thus
5.强调
certainly, above all, indeed, of course, surely, actually, as a matter of fact, especially in particular, absolutely,
6.让步
although, though, after all, in spite of
7.举例
for example, for instance, that is, namely, such as, in other words, in this case, by way of illustration.
8. 时间和空间
afterward, after, first, later, then, soon, finally, at last outside, near, beyond, above, below, on the right(left), in the middle, opposite, in front of
9. 总结
to sum up, to conclude, in a word, in short, in brief, all in all, in all, in summary
非常感谢您的耐心观看,如有帮助请采纳,祝生活愉快!谢谢!
2006年全国普通高等学校招生统一考试
上海英语试卷
本试卷分为第1卷(第1-12页)和第Ⅱ卷(第13页)两部分。全卷共13页。满分150分。考试时间120分钟。
第Ⅰ卷 (共105分)
考生注意:
1. 答第1卷前。考生务必在答题卡和答题纸上用钢笔或圆珠笔清楚填写姓名、准考证号、校验码. 并用铅笔在答题卡上正确涂写准考证号和校验码。
2. 第1卷(1-16小题. 25-84小题)由机器阅卷, 答案必须全部涂写在答题卡上。考生应将代表正确答案的小方格用铅笔涂黑。注意试题题号和答题卡编号一一对应, 不能错位。
答案需要更改时。必须将原选项用橡皮擦去, 重新选择。答案不能写在试卷上。写在试 卷上一律不给分。第1卷中的第17-24小题和第Ⅱ卷的试题, 其答案写在答题纸上, 如写在试卷上则无效。
I. Listening Comprehension
Part A Short Conversations
Directions: In Part A. you will hear ten short conversations between two speakers. At the end of each conversation, a question will be asked about what was said. The conversations and the questions will be spoken only once. After you hear a conversation and the question about it. Read the four possible answers on your paper. and decide which one is the best answer to the question you have heard.
1. A. On March 2. B. On March 3. C. On March 5. D. On March 8.
2. A. At a cinema. B. At an airport. C. At a railway station. D. At a stadium.
3. A. Old castles. B. Hunting games. C. A seaside holiday. D. An adventure.
4. A. By bus. B. By underground. C. On foot. D. By bicycle.
5. A. Go to the movies. B. See a doctor. C. Get some fruit. D. Stay at home
6. A. Car seller. B. Police officer. C. Detective. D. Reporter
7. A. Funny B. crazy. C. Amused. D. P1eased
8. A. They’d better not go riding. B. Riding a bike is a great idea.
C. It’s not good riding in the rain D. They can go riding half an hour later
9. A. There won’t be enough cups left. B. They’ve got plenty of cups.
C. They’re buying what they need. D. They’ve got enough food for the picnic.
10. A. He's unable to finish his homework. B. He can’t give the woman his computer.
C. He's to remove the virus. D. He's infected with some disease.
Part B Passages
Directions: In part B, you will hear two short passages, and you will be asked three questions on each of the passages. The passages will be read twice, but the questions will be spoken only once. When you hear a question, read the four possible answers on your paper and decide which one would be the best answer to the question you have heard.
Questions 11 through 13 are based on the following passage.
11. A. Some engineers. B. The landlord of the pub.
C. The former employees. D. Some customers of the company.
12.A.Threeyears ago. B. Five years ago. C. Last year. D. This year.
13. A. Why a company lost its customers. B. Why a company went out of business.
C. How a company went from bad to worse. D. How a company got out of its difficult situation
Questions 14 through 16 are based on the following report.
14. A. Physics. B. chemistry. C. English Literature. D. Media Studies
15. A. More than 144,000. B. About 147,500.
C. 7.5% of all the test takers. D. 4.6%of all the test takers.
16. A. Few students avoid harder subjects. B. Each subject has the same level of difficulty.
C. Some subjects are more difficult than others. D. Pupils are important to t11e country’s development.
Part C Longer Conversations
Directions: In Part C, you will hear two longer conversations. The conversations will be read twice. After you hear each conversation, you are required to fill in me numbered blanks with the information you have heard. Write your answers on your answer sheet.
B1anks l 7 through 20 are based on the following conversation.
Taxi Order Form
Name: John Smith
Time: 5:30 a.m., ___17___, June 8th
To: The ___18___
From: 99 Kent Street, near Carlington ___19_____
Phone Number: ____20____
Complete the form. Write ONE WORD for each answer.
Blanks 21 through 24 are based on the following conversation.
What does the woman complain about? ______21_______
What does the man suggest the woman do first? She should __22__ all the way to the right.
Why is the engineer sent up? He is __23__ for maintaining buildings.
When is it suitable for the engineer to come? ___24___ later.
Complete the from. Write NO MORE THAN THREE WORDS for each answer.
Ⅱ. Grammar and Vocabulary
Directions: Beneath each of the following sentences there are four choices marked A, B, C and D. Choose the one answer that best completes the sentence.
25. —It’s atop secret. —Yes, I see. I will keep the secret _____ you and me
A. with B. around C. among D. between
26. Black holes ______ not be seen directly, so determining the number of them is a tough task.
A. can B. should C. must D. need
27. Send my regards to your lovely wife when you _______ home.
A. wrote B. will write C. have written D. write
28. A typhoon swept across tiffs area with heavy rains and winds_____ strong as 113 miles per hour.
A. too B. very C. so D. as
29. I made so many changes in my composition mat only I could read it. To ____ else, it was hard to make out.
A. none B. everyone C. someone D. anyone
30. A dozen ideas were considered _____ the chief architect decided on the design of the building.
A. because B. before C. whether D. unless
31. Eugene's never willing to alter any of his opinions. It’s no use ____ with him.
A. to argue B. arguing C. argued D. having argued
32. When he turned professional at the age of 11, Mike _____ to become a world champion by his coach and parents.
A. expected B. was expecting C. was expected D. would be expected
33. Energy drinks are not allowed _____ in Australia but are brought in from New Zealand.
A. to make B. to be made C. to have been made D. to be making
34. Russ and Earl were auto mechanics _____ the same pay, but Earl had more ambition.
A. to earn B. to have earned C. earning D. earned
35. One advantage of playing the guitar is _____ it can give you a great deal of pleasure.
A. how B. why C. that D. when
36. The mother felt herself ____ cold and her hands trembled as she read the letter from the battlefield.
A. grow B. grown C. to grow D. to have grown
37. In an hour, we can travel to places _____ would have taken our ancestors days to reach.
A. where B. when C. which D. what
38. My parents were quarrelling about me ____ I could not quite tell why.
A. since B. though C. if D. until
39. He spoke proudly of his part in the game, without mentioning ____ his teammates had done.
A. what B. which C. why D. while
40. _____ automatically the e-mail will be received by all the club members.
A. Mailed out B. Mailing out C. To be mailed out D. Having mailed out
41. You can see the stars on a clear night, but in the daytime they are _____.
A. unavoidable B. invisible C. inaccessible D. unavailable
42. When Jane began to take swimming lessons, her main _____ was the fear of water.
A. evidence B. crisis C. obstacle D. danger
43. Try not to start every sentence with “the”. _____ the beginnings of your sentences.
A. Vary B. Decorate C. Form D. Describe
44. I hope I will not be called on in class as I’m not yet _______ prepared.
A. attentively B. readily C. actively D. adequately
III. Cloze
Directions: For each blank in the following passages there are four words or phrases marked A, B, C and D. Fill in each blank with the word or phrase that best fits the context.
(A)
Several years ago, well-known writer and editor Norman Cousins became very ill. His body ached and he felt constantly tired. It was difficult for him to even __45__ around. His doctor told him that he would lose the ability to move and eventually die from the disease. He was told he had only a 1 in 500 chance of survival.
__46__ the diagnosis(诊断), Cousins was determined to overcome the disease and survive. He had always been interested in medicine and had read a book, which discussed the idea of how body chemistry and health can be damaged by emotional stress and negative __47__. The book made Cousins think about the possible __48__ of positive attitudes and emotions. He thought, “Is it possible that love, hope, faith, laughter, confidence, and the __49__ to 1ive have positive treatment value?”
He decided to concentrate on positive emotions as a way to treat some of the symptoms of his disease. In addition to his traditional medical treatment, he tried to put himself in situations that would __50__ positive emotions. “Laugh therapy” became part of his treatment. He __51__ time each day for watching comedy films, reading humorous books, and doing other activities that would draw out __52__ emotions. Within eight days of starting his ‘‘laugh therapy” program his pain began to __53__ and he was able to sleep more easily. He was able to return to work in a few months’ time and __54__ reached complete recovery after a few years.
45. A. run B. pass C. move D. travel
46. A. Besides B. Despite C. Without D. Beyond
47. A. attitudes B. beliefs C. goals D. positions
48. A. shortcoming B. harm C. benefit D. interest
49. A. emotion B. pain C. fear D. will
50. A. bring about B. set about C. put up D. make up
51. A. afforded B. appointed C. offered D. arranged
52. A. positive B. approving C. strong D. mixed
53. A. escape B. decrease C. shrink D. end
54. A. generally B. especially C. actually D. presently
(B)
“When a customer enters my store, forget me. He is King, ’’said John Wanamaker, who in l876 turned an abandoned railway station in Philadelphia into one of me world’s first department stores. This revolutionary concept __55__ the face of retailing(零售业) and led to the development of advertising and marketing as we know it today.
But convincing as that slogan was, __56__ the shopper was cheated out of the crown. __57__ manufacturing efficiency increased the variety of goods and lowered prices, people still relied on advertisements to get most information about products. Through much of the past century, ads spoke to an audience restricted to just a few radio or television channels or a __58__number of publications. Now media choice, has __59__ too, and consumers select what they want from a far greater variety of sources—especially with a few clicks of a computer mouse. __60__ the internet, the consumer is finally seizing power.
As our survey shows, __61__ has great implications for companies, because it is changing the way the world shops. Many firms already claim to be “customer-driven” or “consumer-centred”. Now their __62__ will be tested as never before. Taking advantage of shoppers’ __63__ will no longer be possible: people will know—and soon tell others, even those without the internet—that prices in the next town are cheaper or that certain goods are inferior. The internet is working wonders in __64__ standards. Good and Good and honest firms should benefit most.
55. A. changed B. maintained C. restored D. rescued
56. A. in time B. in truth C. in case D. in theory
57. A. Just as B. The moment C. If D. Although
58. A. 1imited B. minimum C. sufficient D. great
59. A. disappeared B. existed C. exploded D. survived
60. A. According to B. Thanks to C. But for D. Apart from
61. A. consumer power B. product quality C. purchasing habit D.manufacturing efficiency
62. A. information B. investment C. claims D. shops
63. A. generosity B. knowledge C. curiosity D. ignorance
64. A. raising B. lowering C. abandoning D. carrying
IV. Reading Comprehension
Directions: Read the following four passages. Each passage is followed by several questions or unfinished statements. For each of them mere are four choices marked A, B, C and D. Choose the one mat fits best according to me information given in me passage you have just read.
(A)
Cara Lang is 13. She lives in Boston, Massachusetts, in me U. S. Last Thursday, she didn't go to school. She went to work with her father instead. Every year, on the fourth Thursday in April, millions of young girls go work. This is Take Our Daughters to Work Day. The girls are between me ages of 9 and 15. They spend the day at work with an adult, usually a mother, father, aunt, or uncle. They go to offices, police stations, laboratories, and other places where their parents or other family members work. Next year, the day will include sons, too.
The Ms. Foundation, an organization for women, started the program about ten years ago. In the U.S., many women work outside the home. The Ms. Foundation wanted girls to find out about many different kinds of jobs. Then, when the girls grow up, they can choose a job they like.
Cara's father is a film director. Cara says, “It was very exciting for me to go to the studio with my dad. I saw a lot of people doing different jobs.” Many businesses have special activities for girls on this day. Last year, Cara went to work with her aunt at the University of Massachusetts. In the engineering department, the girls learned to build a bridge with toothpicks and Candy. In the chemistry department, they learned to use scales. They learned about many other kinds of jobs, too.
Right now, Cara does not know what job she will have when she grows up. But because of Take Our Daughters to Work Day, she knows she h2Ls many choices.
65. What is Cara's father?
A. An engineer. B. An official. C. A moviemaker. D. A professor.
66. According to the passage, Take our Daughters to work Day is ______.
A. on every Thursday in April B. a holiday for girls of all ages
C. a day for girls to know about jobs D. a day for girls to get a job easily
67. On this special day, Cara has done all the following EXCEPT that ____.
A. she learned to use scales B. she worked as an actress
C. she went to work with her aunt D. she used toothpicks and Candy to build a bridge
68. What is probably the best title for the passage?
A. Cara Lang, a Fortunate Girl B. Take Our Daughters to Work Day
C. Children's Day and Work Day D. Ms. Foundation, an Organization for Women
(B)
Nervous suspects(嫌疑犯) locked up in Britain's newest police station may feel relieved by a pleasant yellow Colour on the door. If they are close to confessing a crime, the blue on the wall might tip the balance.
Gwent Police have abandoned colours such as greys and browns of the 20th-century police cell(牢房) and have used colour psychology to decorate them.
Ystrad Mynach station, which recently opened at a cost of£5 million, has four cells with glass doors for prisoners who suffer from claustrophobia(幽闭恐怖症). Designers have painted the frames yellow, which researchers say is a calming colour. Other cells contain a royal blue line because psychologists believe that the colour is likely to encourage truthfulness.
The station has 31 cells, including 12 with a “live scan” system for drunken or disturbed prisoners, which detects the rise and fall of their chest. An alarm alerts officers if a prisoner's breathing stops and carries on ringing until the door is opened.
Designers and psychologists have worked for years on colour. Blue is said to suggest trust, efficiency, duty, logic, coolness, thinking and calm. It also suggests coldness and unfriendliness. It is thought that strong blues will stimulate clear thought and lighter, soft colours will calm the mind and aid concentration.
Yellow is linked with confidence, self-respect and friendliness. Get the colour wrong and it could cause fear, depression and anxiety, but the right yellow can lift spirits and self-respect.
Ingrid Collins, a psychologist who specializes in the effects of colour, said that colour was an “energy force”. She said: “Blue does enhance communication but I am not sure it would enhance truthful communication.”
Yellow, she said, affected the mind. Red, on the other hand, should never be considered because it could increase aggression. Mrs Collins praised the designers for using colours in the cells. Gwent is not the first British force to experiment with colour to calm down or persuade prisoners to co-operate. In the 1990s Strathclyde Police used pink in cells based on research carried out by the US Navy.
69. The expression “tip the balance” in paragraph 1 probably indicates that the blue might ____.
A. let suspects keep their balance B. help suspects to confess their crimes
C. make suspects cold and unfriendly in law court D. enable suspects to change their attitudes to colours
70. Which of the following colours should NOT be used in cells according to me passage?
A. Pink. B. Yellow C. Blue. D. Red.
71. Which of the following helps alert officers if someone stops breathing?
A. Scanning equipment. B. Royal blue lines. C. Glass doors. D.Yellow frames.
72. The passage is mainly concerned with ______
A. the relationship between colours and psychology B. a comparison of different functions of colours
C. the use of colours in cells to affect criminals’ psychology
D. scientific ways to help criminals reform themselves in prison
73. The word “talion” in introducing the book Eye for an Eye is probably a concept of ______.
A. medicine B. trade C. avenging D. striving
74. The book entitled A History of Modern Indonesia has focus on _______.
A. 1andscapes and tourist attractions in Indonesia B. its fourth largest population in the world
C. its relatively unfamiliar and understudied economy D. its social and political aspects in modern times
75. What do these books have in common?
A. Their authors are introduced in detail. B. They all have a hard back and a paperback.
C. Each of them is commented by a professor. D. They are published by the same publishing house.
(D)
The “Bystander Apathy Effect” was first studied by researchers in New York after neighbours ignored—and in some cases turned up the volume on their TVs—the cries of a woman as she was murdered(over a half-hour period). With regard to helping those in difficulty generally, they found that:
(1) women are helped more than men;
(2) men help more than women;
(3) attractive women are helped more than unattractive women.
Other factors relate to the number of people in the area, whether the person is thought to be in trouble through their own fault, and whether a person sees himself as being able to help.
According to Adrian Furnham, Professor 0f University College, London, there are three reasons why we tend to stand by doing nothing:
(1) “Shifting of responsibility”一the more people there are, the less likely help is to be given. Each person excuses himself by thinking someone else will help, so that the more “other people’ there are, the greater the total shifting of responsibility.
(2) “'Fear of making a mistake'’一situations are often not clear. People think that those involved in an accident may know each other or it may be a joke, so a fear of embarrassment makes them keep themselves to themselves.
(3) “Fear of the consequences if attention is turned on you, and the person is violent.”
Laurie Taylor, Professor of Sociology at London University, says: “In the experiments I’ve seen on intervention(介入), much depends on the nei